-

RTM 2200 – Radon and Thoron Measurement System
11.949,00€ Inc. VAT: 14.577,78€ Sold By : Niton Srl
Add to cart -

RTM 2200 Soil Gas – Radon and Thoron Monitor with Integrated Measurement of the Soil Permeability
13.949,00€ Inc. VAT: 17.017,78€ Sold By : Niton Srl
Add to cart -

RAD7 Radon Detector – Real-time Continuous Radon Monitor
7.699,00€ Inc. VAT: 9.392,78€ Sold By : Niton Srl
Add to cart -

RTM 1688-2 – Radon and Thoron Monitor
8.150,00€ Inc. VAT: 9.943,00€ Sold By : Niton Srl
Add to cart
With this new tool, it is easy to estimate the amount of Radon that could transfer to the environment based on the amount of Radon dissolved in water 💧. This new tool is available now on AppoRad under the Radon Tools section: Radon in water to Radon in air
The unit of measurement for Radon in the water is Bq/L or pCi/L in water. After the concentration of Radon in water is measured in one of the mentioned units, you just need to put the measured value in the converter, and AppoRad gives you the result.
🔔 Please note that the result shows on AppoRad is an average value and could be vary based on the amount of water is used, ventilation of the building, and many other factors.
Reza Hosseini, PhD - Managing Director at RadonMarket, R&D Manager & NRPP MFM Certified Radon Professional at Niton srl
If you follow our short article series (RADON IN PILOLE 💊), you may remember that we have talked about the four main ways Radon enters buildings. Among these four, Radon coming inside buildings from gas soil due to convection has a significant 85-90% contribution role. Instead, Radon from water contributes less than 1%. Hence, Radon mitigators mainly deal with the methods to reduce the Radon coming from the soil. Still, to achieve an acceptable Radon indoor level, Radon in water should also be reduced in some cases.
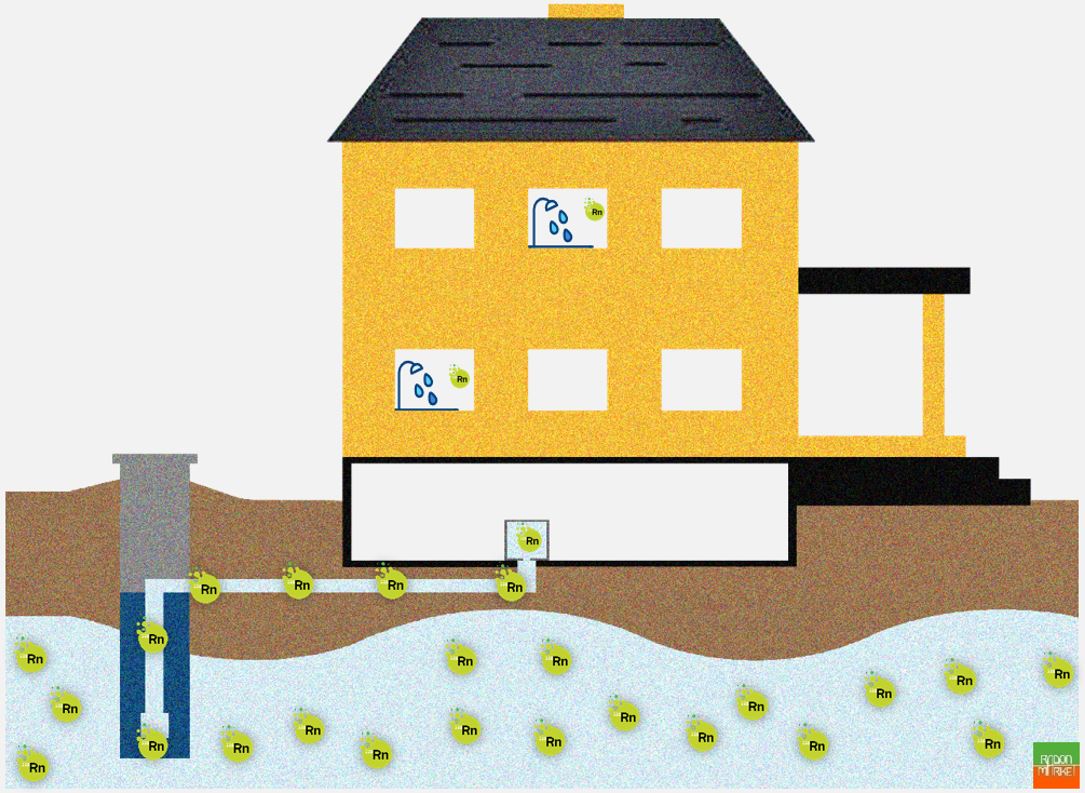
Reducing Radon in water is a complicated topic and needs skills in different areas, from plumping to water quality. We will discuss Radon in water in two numbers of RadonMarket Mag. in this number, we will see:
✅ How Radon goes in the water initially?
✅ Is the contribution of Radon in water significant?
✅ Notes For Radon Professionals, "What should be considered when dealing with Radon in water?"
In the next number, we will discuss the methods of Reducing Radon in water.
✅ How Radon goes in the water initially?
The same Radium source that causes Radon in the gas soil could be in contact with the water in the aquifer. As Radon is very soluble in water, it can enter and dissolve easily in the aquifer. In this situation, a well that brings water from the aquifer directly to the house could also bring the Radon inside it. As the Half-life of Radon is 3.8 days, it can travel for a long distance inside the pipes and reaches even higher floors. Radon can cause lung cancer when we breathe its decay products suspended in the air, but no evidence shows a significant health risk when we drink Radon dissolved in water. So how Radon in water could be a health risk?
If you don't remember the health effect of Radon, watch the videos of this Free course on RadonMarket Academy.
 Actually, Radon in water could be a health risk only when the dissolved Radon comes out of the water as soon as it reaches the atmospheric pressure and diffuses inside the closed area of a building. For example, it could happen when the water is used for the shower or the dishwasher. Like any other dissolved gas, Radon tends to come out of the solution at a higher temperature, for example, a shower with hot water. The Radon that comes out of the water solution then adds to the Radon coming directly from the soil (or from other sources) and increases the Radon concentration level inside the building.
Actually, Radon in water could be a health risk only when the dissolved Radon comes out of the water as soon as it reaches the atmospheric pressure and diffuses inside the closed area of a building. For example, it could happen when the water is used for the shower or the dishwasher. Like any other dissolved gas, Radon tends to come out of the solution at a higher temperature, for example, a shower with hot water. The Radon that comes out of the water solution then adds to the Radon coming directly from the soil (or from other sources) and increases the Radon concentration level inside the building.
✅ Is the contribution of Radon in water significant?
The unit of measurement for Radon in the water is Bq/L (pCi/L in water). On average, 1000 Bq/l of Radon in the water can add 100 Bq/m3 to the overall indoor Radon level (10,000 pCi/L in water can yield around 1 pCi/L into the air). Please consider that this is an average value and could be vary based on the amount of water is used, ventilation of the building, and many other factors.
To see how we can calculate the significance of the contribution of Radon in the water compared to the overall Radon concentration inside a building, we make an example:
🤷 Inside a house, it measured 500 Bq/m3 of indoor Radon. A separate test is performed to measure the Radon in water, and the result shows 1500 Bq/l. What is the primary source of indoor Radon for this building? ✏ The contribution of Radon in the water is about 150 Bq/m3. ✏ Therefore the contribution of Radon coming from another source (More likely from the soil) is 350 Bq/m3. Use AppoRad to do these calculations. Read more at the end of this document! Looking at the measured values, it seems that the primary source of Radon in that building is the water supply. However, as demonstrated above, from the total 500 Bq/m3 Radon concentration, 350 Bq/m3 is from another source (more likely from the soil). |
The Radon in water could play a significant role depending on the level of Radon in the water, amount of water usage, and the level of Radon coming from other sources. Typically, reducing Radon coming from the soil gas has the most significant impact on lowering indoor Radon levels. Moreover, considering the complication of the techniques to reduce Radon in the water supply, it is always recommended to start working on the Radon in soil gas for a mitigation project.
✅ Notes For Radon Professionals: "What should be considered when dealing with Radon in water?"
📝 The Radon inside a building could come from different sources, like soil, water, or emanation from building materials. Therefore, even though Radon coming from water does not represent a significant fraction of Radon in most cases, a Radon professional must consider these other possibilities. 📝 Buildings with groundwater supplies, especially homes with a private well, can have elevated Radon in well water. 📝 Radon moves by water, and it can go out of the pipes anywhere. In RADON IN PILOLE 💊 series, we mentioned that we might need to measure Radon level in higher floors for a complete diagnostic. Radon in water is one of the reasons! 📝 When the water is using in an open area like for gardening, the presence of Radon in water may not be a problem. Instead, when Radon can go out of water in a closed space and have time to be accumulated, we could consider it a health risk. 📝 Radon goes out of water when someone uses the water! Therefore the measurement in a building without occupation does not represent the contribution of Radon in water and its potential health risk. 📝 Using a continuous Radon monitor (CRM) could be very helpful to do a diagnostic. An increase in the Radon level could be detectable with these types of instruments each time hot water is used for a while. Even though it is not generally recommended to put CRMs inside the bathroom, it could not be a bad idea to use them for diagnostic purposes. |
Reza Hosseini, PhD - Managing Director at RadonMarket, R&D Manager & NRPP MFM Certified Radon Professional at Niton srl
In the last number of RadonMarket Mag we have talked about Radon in water. We have seen "How does Radon initially dissolve in water?", "How to evaluate the contribution of water in the increase of Radon in the air?" and "What to keep in mind when dealing with the Radon problem in water?". In this article, we continue our discussion, and we will review the most common methods to reduce the concentration of Radon activity in water. If you missed the previous number of RadonMarket Mag (n° 14), please read it before starting this one.
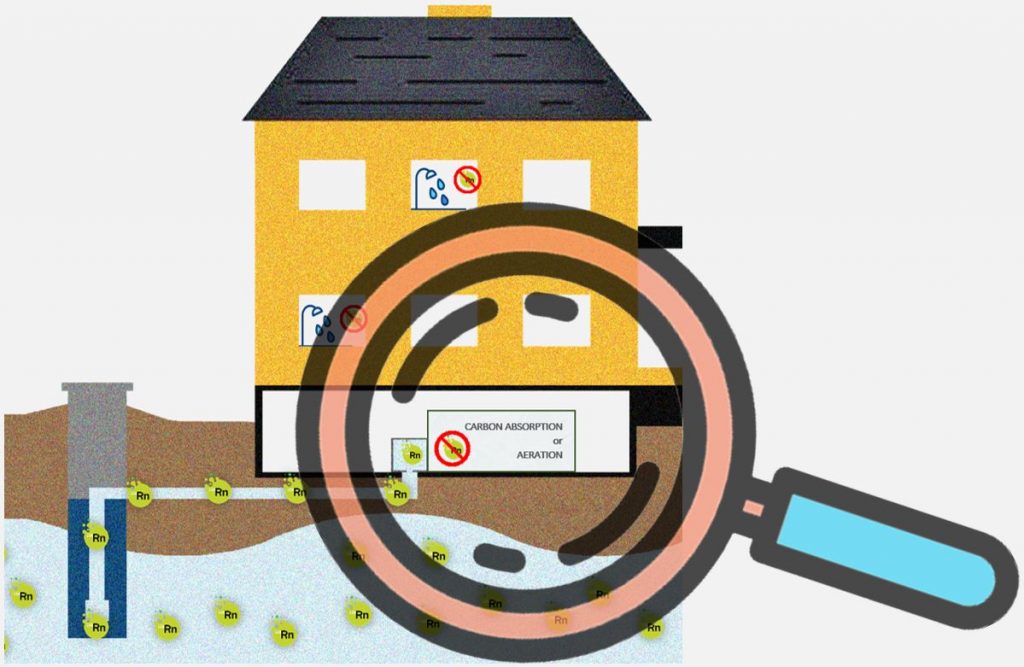
Radon presente nell’acqua di pozzo che contribuisce al livello generale di Radon indoor
Practically there are three ways to reduce Radon in water:
✅ Surface and Decay Storages
✅ Carbon Absorption tanks
✅ Aeration systems
✅ Surface and Decay Storages
On the contrary of well water, surface water typically does not present a Radon in water concern. This is because there is enough residence time for Radon to off-gas and gradually dilute in an open environment as well as decay to Radon Decay Products (RDPs) product 🔔.
🔔 Ingestion of the RDPs not considered to be a significant health concern.
|
Similarly, storing well water in a reservoir could reduce the Radon in water and consider as a mitigation technique. In many public water supplies, groundwater is pumped to the atmospheric storage before it pumps again to consumers' houses. The private wells usually do not have a reservoir tank, and putting one is expensive and impractical. Hence, storage might not be a solution to mitigate Radon in water for individual wells.
As a general rule, homes at the far ends of the distribution network can have less Radon as more residence time allows Radon to decay to RDPs. On the other hand, when water usage goes up, the residence time goes down, and consequently, there is less time for Radon to decay.
✅ Carbon Absorption
Radon could adsorb onto activated charcoal due to physical adsorption or so-called physisorption. The fundamental interacting force of physisorption is Van der Waals 🔔. The Charcoal Canisters for short-term Radon measurements are operate based on physisorption 🔔🔔.
🔔 If you are interested to know more about physisorption, read this article on Wikipedia. 🔔🔔 The charcoal canisters are 4-inch open-face canisters. They consist of a metal canister filled with activated charcoal that is held in place by a wire mesh screen and spring clip. The Radon gas and some of the progeny attach to the charcoal surface. At the end of the testing, the canister is sealed and returned to the laboratory for processing and analysis.
|
Applying the same concept makes it possible to catch Radon in water by running the water through a larger tank fill with Granular Activated Charcoal (GAC). Remember that this is different from the small filters commonly put on the faucets to clean and improve water taste. For reducing Radon in water, the carbon tank should be big enough to support all the water usage of a house (except the water need for gardening or use in open spaces). In addition, the tank should be installed at the entry point of the water supply.
When Radon is absorbed onto the charcoal, it breaks down into RDPs, and the produced RDPs are retained inside the tank. This maintains the concentration gradient between the Radon in water and the surface of the charcoals. Therefore, it creates a sort of self-cleaning system, and Radon can adsorb onto charcoal forever. However, there is a critical issue prevent the unlimited usage of the carbon tank! If you have read our previous articles, it may not be difficult to guess what this preventing reason is?
Clearly, the first reason could be clogging. Even though these systems have filters for removing the particles from the water, eventually, the dirt accumulates inside the tank, and the tank should be replaced. Still, the reason that may concern us more is the Gamma radiation!
As Radon decays inside the tank, it releases alpha, beta, and Gamma. The alpha and beta can not get out of the tank, but gamma certainty can. By accumulating the RDPs inside the tank, gamma emissions increase and become more significant 🗯. Of course, no one wants to keep a tank with radioactive material emitting Gamma radiation inside their house. Hence, carbon tanks are typically replaced yearly to prevent this issue.
🗯 The amount of Gamma that could be emitted from these tanks is 1 mR/hr per 370 Bq/L in water (10000 pCi/L in water). Hence, these systems are not generally recommended for Radon in water with a concentration greater than 370-740 Bq/L (10-20000 pCi/L in water) as a means to limit Gamma emission. 🤷 What happens when carbon tanks are taken out of service? |
Besides the complication that this method introduces, it is a valid technique for reducing the Radon in water. Moreover, there are also other advantages of using carbon, like reducing the odor and improving water taste.
✅ Aeration
We have seen that the dissolved Radon easily gets out of the water and becomes a health risk when we use showers. So why not apply the same mechanism to reduce the Radon in water? This is exactly what happens in an aeration system.
In the aeration method, water from the well is sprayed into a tank, similar to a mini shower. At the same time, or by bellowing air with a pump or by making air bubbles inside the tank, Radon strips out from the water. Then the released Radon exhaust out of the house.
Aeration system also has its own limitations.
🔵 Like an Active Soil Depressurization (ASD), the discharge point for an aeration system should be located in a proper place to prevent exposing people to high Radon concentrations. In addition, because of the high humidity of the exhausted air from an aeration system, special attention is needed for the possible condensation problems.
🔵 On the contrary to carbon absorption, the aeration method puts water at atmospheric pressure. Therefore, an additional pressure tank and pump are needed to distribute water throughout the building.
🔵 The biggest concern in aeration systems is water quality. Blowing air through water could introduce bacteria and other organisms. For this reason, the source of the incoming air should be clean, and the air should pass through proper filters before contacting with water. In order to improve the water quality, especially when water is not in use continuously, an aeration system may also be equipped with a pre or post-disinfection with chlorine or post-disinfection with ultra-violet light systems.
| ☢ As a final comment, we can say that reducing Radon in water is a much expensive and complex project compared to a standard ASD system. Besides lowering the Radon, special attention needs to guarantee the quality of the drinking water. Therefore, when Radon in water is a concern, it is always recommended to ask for help from both Radon and water quality specialists. |











